What are AWS Data Lakes?

Quick Answer: Data lakes are centralized storage repositories that hold vast amounts of raw data in their native format, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. They allow organizations to store everything without schema requirements.
Too much information can be a real problem, especially for those responsible for handling the burgeoning digital data in cyberspace. But thanks to the development of data lakes, cloud data professionals now have the wherewithal to store and manage large datasets to help make sense of all that information.
What are Data Lakes?
Let’s cut right to the chase. A data lake is a centralized repository for data. Just as a lake accumulates water from the various streams and tributaries that feed into it, a data lake acts as a reservoir to hold various types of data from multiple sources. Data lakes can grow to be quite large, without the limitations of traditional databases.
Data lakes are not only scalable and flexible but can also be cost-effective. By leveraging low-cost storage solutions like Amazon S3 and the cloud’s pay-as-you-go pricing, organizations can build affordable data lakes that support their big data analytics needs.
Data Lakes vs. Data Warehouses
But a data lake is not just another place to put your SQL database. Unlike data warehouses, data lakes can store structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data in various forms. Raw, unprocessed data that is dumped into a data lake remains there in its native format, awaiting further processing or transformation when you are ready. It’s an ideal solution for data scientists or machine learning engineers.
The key difference is that data warehouses store cleaned and organized data for specific use cases, while data lakes store everything, ready or not, for broader, more exploratory analysis.
AWS Data Lake Architecture
Key components of an AWS Data Lake architecture include Amazon S3, AWS Glue, Lake Formation, and your favorite analytics tool, such as Athena. Amazon S3 provides a solid foundation for storage in an AWS Data Lake. It is scalable, secure, and with eleven nines of durability (99.999999999%).
Below is a sample data lake architecture. AWS Lake Formation helps create, manage, and optimize data lakes. AWS Glue acts on the data in a process known as extract, transform, and load (ETL). Athena can be used to query and analyze data in SQL fashion. Sources can be in many forms, such as Excel, CSV, or Amazon RDS. Other AWS services can integrate with Data Lakes, such as Lambda or Redshift.
To learn more about data management on Amazon Web Services, consider taking the CBT Nuggets course AWS Certified Data Engineer - Associate (DEA-C01) Online Training. You’ll learn about AWS Data Lakes and much more!
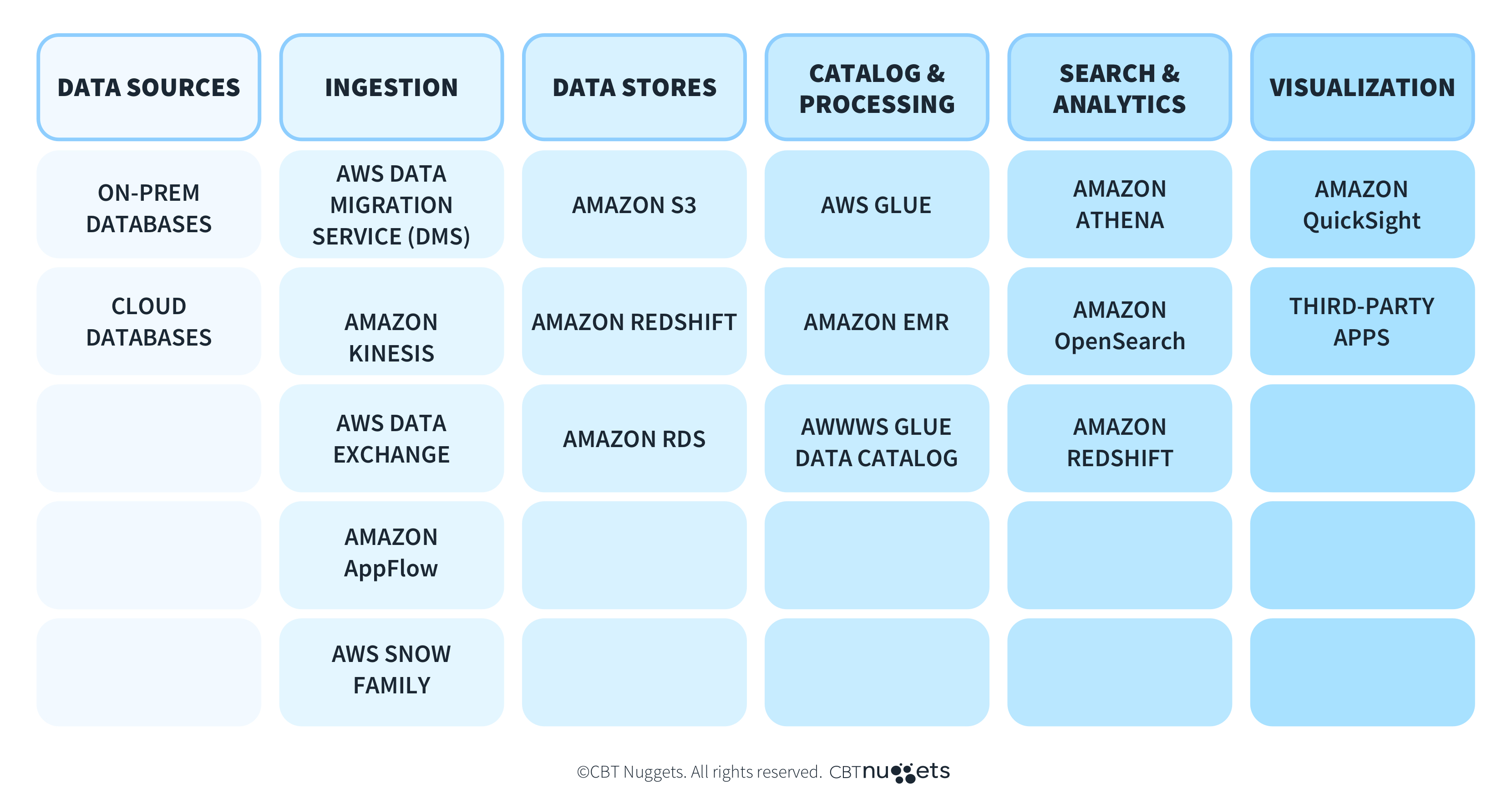
AWS Data Lakes Data Flow
The flow of data in an AWS Data Lake solution can take many twists and turns. The data can be pulled from many different sources, both internal and external. The desired end result will be valuable insights that can be used in business intelligence and decision-making, often fashioned as a comprehensive visual display. Along the way, data can be shaped and coaxed based on varying requirements.
The data flow has six phases, each represented in the columns below along with potentially related AWS services.
Data Sources >>> | Ingestion >>> | Data Stores >>> | Catalog & Processing >>> | Search & Analytics >>> | Visualization |
On-prem databases | AWS Data Migration Service (DMS) | Amazon S3 | AWS Glue | Amazon Athena | Amazon QuickSight |
Cloud databases | Amazon Kinesis | Amazon Redshift | Amazon EMR | Amazon OpenSearch | Third-party apps |
| AWS Data Exchange | Amazon RDS | AWS Glue Data Catalog | Amazon Redshift |
|
| Amazon AppFlow |
|
|
|
|
| AWS Snow Family |
|
|
|
|
AWS Data Lake Best Practices
To make data storage work effectively in an AWS Data Lake, Amazon recommends the use of four distinct S3 buckets. These buckets keep data separate based on content or stage of development:
Raw: Data can be ingested from many different sources and include various data types, such as JSON, CSV, XML, text files, or images. These raw data formats represent immutable copies of the data.
Transformed: Transformed data should be stored in a separate bucket. This may include data that, in its newly transformed state, can be easily queried by Athena.
Curated: Data can be further analyzed and refined, and this should also be stored separately.
Logs: Related CloudWatch and CloudTrail logs can be stored here.
Data ingestion should include implementing data validation and quality checks. All of these data traffic flows should be tracked for optimization and accuracy.
Managing Costs Effectively
AWS Data Lake designers should be mindful of Amazon S3 lifecycle policies and how to implement them wisely. The automatic movement of older data to less expensive S3 tiers can save a lot of money in the long run. Amazon S3 storage classes have different use cases and can be configured using S3 intelligent-tiering.
Essential AWS Data Lake Security Measures
The same security practices used throughout the AWS cloud infrastructure apply here. Data access controls such as S3 bucket policies, access control lists (ACLs), and Amazon Key Management ervice (KMS) keys should be used to keep AWS Data Lakes secure. IAM identities, roles, and policies should control permissions for the use of data lake components.
Compliance and Governance
Data storage, transmission, and use are subject to local, regional, and national jurisdictions, including applicable regulatory requirements. Healthcare and financial institutions are particularly scrutinized regarding privacy (e.g., HIPAA and Sarbanes-Oxley), and Europe has its own special rules (GDPR).
Why Data Lakes Matter for Your Career
Understanding how data lakes work (and when to use them) can give you a serious edge in today’s data-driven IT landscape. Whether you're building your certification roadmap or diving into hands-on roles, data lakes are a key concept worth mastering.
Certification Relevance
If you are interested in AWS certifications, learning more about data lakes will come in handy. Both AWS Data Lakes and AWS Lake Formation are in scope for several AWS certifications, including:
Not sure which certification to pursue in 2025? Our post Top 3 Cloud Certifications to Earn in 2025 may help you decide.
Real-World Applications
AWS Data Lakes are crucial for several types of IT professionals, including cloud data engineers, data scientists, and machine learning engineers. They can help those who want to gain insights into data. They can also be crucial for analyzing data in healthcare, finance, retail, or the Internet of Things (IoT).
Conclusion
Along with other aspects of information technology, data management continues to evolve. An AWS Data Lake provides a robust, secure, and flexible answer to the exponential growth of data and the need to deftly parse and analyze it quickly.
Whether structured or unstructured, raw data ingested into a data lake can then be processed in myriad ways without tampering with the original data source. A good understanding of AWS Data Lakes can be an essential arrow for your expanding quiver of IT skills.
Learn more with Scott Pletcher in our AWS Certified Data Engineer - Associate (DEA-C01) Online Training course.
delivered to your inbox.
By submitting this form you agree to receive marketing emails from CBT Nuggets and that you have read, understood and are able to consent to our privacy policy.