Link State vs Distance Vector vs Hybrid Routing Protocols

Quick Answer: Link state, distance vector, and hybrid routing protocols all help transmit traffic across the network as efficiently as possible. Each has advantages and disadvantages and should be evaluated prior to deployment.
If you’ve ever been on a road trip, you have probably planned the most efficient route to your destination. For example, if you’re driving from New York to Florida, it’s unlikely you will pass through Kansas along the way. Computers and networking equipment operate similarly, seeking the most efficient path to their destination.
While you might use Google Maps or Apple Maps to plan your route, networks use protocols to determine the most efficient paths for data transmission. This article will discuss three of the most common routing protocols used in modern networking architecture.
We’ll compare and contrast link state, distance vector, and hybrid routing protocols. We’ll also look at each protocol's benefits and drawbacks and discuss which scenarios might benefit from it.
What are Link State Routing Protocols?
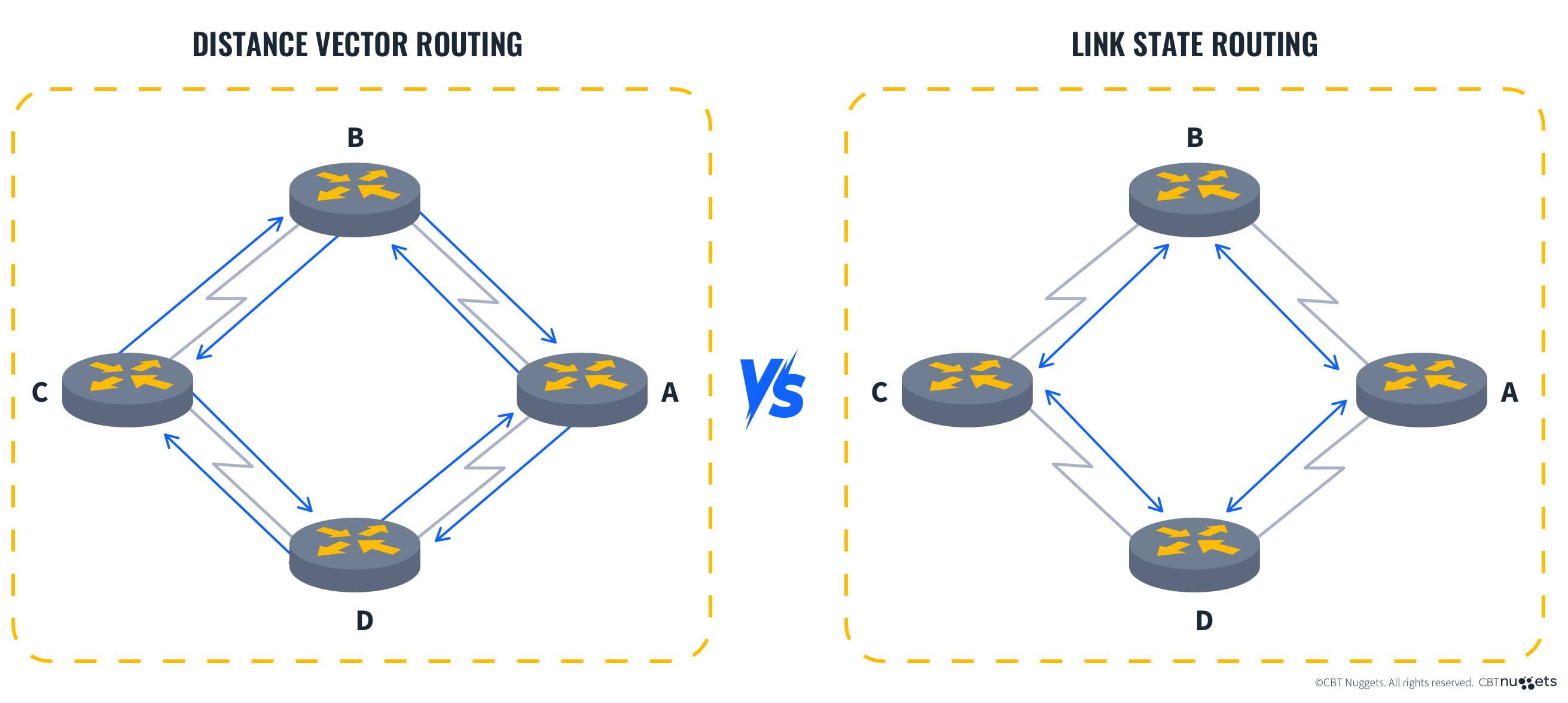
Link state routing protocols like OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) and IS-IS (Intermediate System to Intermediate System) work by having nodes advertise themselves and their path to the destination so all possible routes can be evaluated.
If we refer back to our earlier example of a road trip, link state routing protocols work similarly to how Google Maps or Apple Maps show you the most common paths. You might notice that while taking the highway adds mileage to your trip, it reduces your total travel time compared to if you were to take back roads, or vice versa.
Let's look specifically at the OSPF protocol, which is an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP). The OSPF protocol works by having all networking devices preserve a copy of the network’s topology and its place within it. This information is referred to as link-state advertisements or LSAs.
This helps each device determine the shortest path going forward. OSPF updates incrementally, meaning devices will only update their LSAs for the modified sections of topology when those modifications occur.
The IS-IS protocol similarly updates incrementally, is an interior gateway protocol, and uses the SPF (shortest path first) algorithm to determine the most efficient route.
Think of these protocols similarly to how your navigation app of choice makes updates. Rather than updating your app every single time you use it to determine which roads are closed or are experiencing delays, the app updates that information for you as changes occur.
These protocols have a few advantages over their distance vector routing protocols, which we will discuss in the next section. For one, the IS-IS protocol scales well, and it even scales better than the OSPF protocol. Both the IS-IS and OSPF protocols offer faster convergence and consume less bandwidth than the distance vector routing protocols.
What are Distance Vector Routing Protocols?
In contrast to link state routing protocols, where nodes advertise themselves in a way that provides a map of the overall network topology, distance vector routing protocols advertise themselves one node at a time.
Additionally, these advertisements are often referred to as “routing by rumor” because nodes share information with each other and do not know where the information comes from. It’s like a giant game of telephone where each device isn’t entirely sure the information they’ve been given is accurate.
Referring back to our road trip example, imagine that instead of viewing the whole journey, your navigation app told you to take a route by calculating a bunch of short journeys. Instead of taking a major highway for 50 miles to reach your destination, you end up taking a handful of back roads that are only 4 to 7 miles long, but the total mileage adds up to 60 miles in the end. That’s distance vector routing – you’ve taken the shortest paths between individual devices but not necessarily the shortest path overall.
What are Hybrid Routing Protocols?
As the name suggests, hybrid routing protocols employ the best parts of both link state and distance vector protocols to provide the shortest and most reliable paths for network traffic. Hybrid network protocols are often used by entities such as universities, Internet Service Providers (ISPs), and even large event spaces. Hybrid routing protocols help the network adjust to rapid surges in users.
Some examples of hybrid routing protocols include Cisco’s Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) and the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). EIGRP combines the fast convergence speeds of link state routing protocols and the easy setup of Distance Vector protocols. Similarly, BGP works to find the ideal path for network traffic to travel.
Link State, Distance Vector and Hybrid Routing Protocols: Main Differences
The main advantage of distance vector routing over link state routing protocols is the ease of setup and maintenance, as well as low resource utilization. Link state routing protocols also have the advantages of faster convergence, more accurate network topology, and not being susceptible to the “count to infinity” problem, which is an issue with the use of the Bellman-Ford Algorithm Distance Vector routing protocols.
Of course, hybrid routing protocols offer the most advantages of all protocols. Starting with the fastest convergence, hybrid protocols also consume less bandwidth than link-state protocols and only update upon network changes, compared to the full periodic updates that come with distance vector routing protocols.
Hybrid routing protocols also support load balancing, which is unsupported by distance vector routing protocols.
What are Some Considerations for Network Engineers?
So, which routing protocols should you, as a network engineer or architect, implement within your environment? When selecting routing protocols, you will want to consider factors like the size of your network, whether you will be scaling that network, the topology, and desired performance.
Here’s a chart to help compare some of the different strengths and weaknesses of link state, distance vector, and hybrid routing protocols:
Feature | Link State | Distance Vector | Hybrid |
Bandwidth Use | Consumes less bandwidth. | Consumes the most bandwidth of the three. | Consumes less bandwidth. |
Update Size | Incremental changes only | Full updates | Incremental changes only |
Supports Load Balancing? | Yes | No | Yes |
CPU / RAM Consumption | Highest consumption of the three. | Least consumption of the three. | Consumes less than Link State, but more than Distance Vector |
Convergence | Moderate speed | Slow | Fast |
Optimal Network Size | Works well with most network sizes | Best for smaller networks | Works well with most network sizes |
Using this as a starting point, you should be able to determine which protocol might best fit your network’s needs.
Conclusion
There are many options when it comes to networking, and one of those options includes the type of routing protocols network engineers and architects can choose from when setting up a network.
When selecting from the three main routing protocols, you will need to determine whether link state, distance vector, or hybrid routing protocols will be the best fit for your network's needs. While they each have their own advantages and disadvantages, consider factors such as what type of performance you need, how much resource utilization you can tolerate, and whether you are likely to need load balancing.
To learn more about preparing for a network deployment, take our CompTIA Network+ training course.
delivered to your inbox.
By submitting this form you agree to receive marketing emails from CBT Nuggets and that you have read, understood and are able to consent to our privacy policy.