What is Dual Ring Topology?

Quick Definition: Dual ring topology is a network configuration featuring two interconnected rings, allowing data to flow in opposite directions for enhanced reliability and fault tolerance. It is commonly used in critical infrastructure where uptime is crucial, as it can automatically switch to the secondary ring in case of a failure on the primary ring.
While it provides redundancy and high availability, dual ring topology may become complex and costly with limited scalability as more devices are added, but it offers a robust solution for smaller-sized networks that require redundancy and simple failover.
Dual ring topology is a network configuration of two interconnected rings. These rings send communication from one computer to another. The second ring is a backup. With that 1,000 foot view in mind, let’s walk through the definition of dual ring topology and learn more about ring networks themselves.
If you're studying for Network+ certification, understanding network topologies is a fundamental step toward becoming a successful network engineer. There are many different types of network configurations, such as star, bus, ring (including dual ring), tree, and mesh. Each of these topologies has different features that allow you to map and manage your network based on your needs.
There are pros and cons to each type of network topology, but knowing more about how each is arranged can help you map and manage network configurations based on the particular requirements of your business.
What is Dual Ring Topology?
When it comes to computer networks, the efficiency and reliability of data transmission are paramount. One network topology that has garnered significant attention for its robustness and fault tolerance is the dual ring topology. Let’s discuss the basics of network topology and ring networks before diving more into what dual ring topology really means.
What is a Network Topology?
Network topology is a term used to describe the physical or logical arrangement of devices on a computer network. There are myriad ways to connect a network topology, including bus, mesh, star, etc.
In short, a network topology describes how computers will be set up to facilitate communication. Generally, network engineers will use numerous criteria to determine which topology best suits their purpose. Some of those criteria include the amount of physics space, the number of nodes on the network, budgetary constraints, and more.
What is a Ring Network?
A ring network is a method of laying out a network that ensures predictable and equitable access to network resources. Each device is connected to exactly two other devices. The data will generally only flow in one direction.
Dual topology works similarly to ring topology. The difference is that dual ring topology has two rings instead of one, each sending data in opposite directions. It’s generally used on critical infrastructure when uptime is of the utmost importance.
How Dual Topologies Work
How dual topologies work is actually fairly straightforward. It is one of the earlier topologies, but its reliability and simplicity have made it a timeless choice for network engineers.
Moreover, the supplementary ring of communication has bolstered its resilience, allowing it to withstand the test of time.
5 Components of a Dual Ring Topology
There are several components of a dual ring topology. The first one is the primary ring.
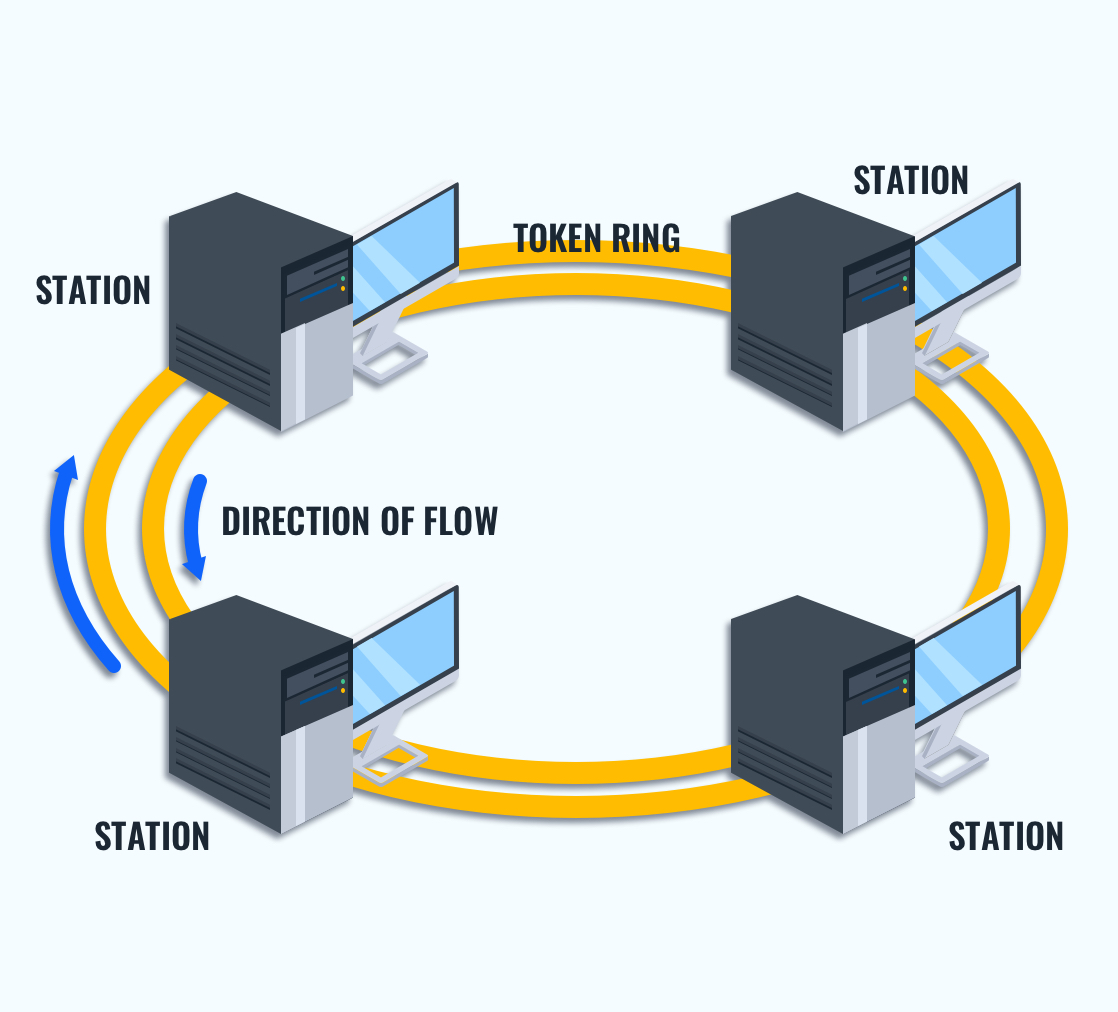
The primary ring is a uni-directional data flow path that enables communication between network devices. The ring is made of CAT5 cables connected to different devices.
Next is the secondary ring. The secondary ring gives the topology its name: dual ring topology. The secondary ring is a failover circuit in case the first one breaks. For example, if a computer crashes on the network, the secondary circuit will be activated, and the data packets will travel in the opposite direction.
The devices themselves constitute the next component of a dual ring topology. A device can be anything with a network interface card (NIC). Each device is connected to two neighbors and passes the data along to the next neighbor in a uni-directional manner. This creates a ring with another ring of connectivity for the secondary ring.
Next comes tokens. The tokens ensure stable communication through the network. Think of it as a “talking stick” in a group therapy session. A talking stick ensures that no one is interrupted so that proper communication can take place.
In IT, the computer possessing the token is granted priority in data transmission. This eliminates the possibility of data collision. Once the node has transmitted everything it needs to, it passes the token to the next computer.
Lastly, switches and ethernet hubs are used on a ring topology to ensure data is properly transmitted to the correct nodes. For example, a computer in a dual ring topology could be connected to two switches on either side of it.
To sum it up, the following make up the components of a dual ring topology:
Primary Ring
Secondary Ring
Nodes
Tokens
Switches/Routers
Primary and Secondary Rings Create Redundancy
There is a redundancy mechanism of dual ring topology— but this is arguably its most important advantage. One of the disadvantages of a standard ring topology is that if one computer goes down, that means the whole network goes down with it.
The addition of a secondary ring resolves this issue. In case of failure, the network will use the backup ring, and the data will flow in the opposite direction. The topology can detect when a connection is broken and automatically route packets in the opposite direction using the secondary ring.
Benefits of Dual Ring Topology
There are numerous benefits of dual ring topology. Let’s walk through each of them and how they can benefit your organization.
Redundancy and Fault Tolerance
Just like a spare tire helps you get home in case of a flat, the fault tolerance provided by dual ring topology works to keep downtime to a minimum in case disaster strikes. First, data flows normally in one direction, and the secondary rings sit idle. But if a catastrophe occurs when your coworker Bill spills coffee on a computer and shorts it out, you'll have a fail-safe in place.
In the case of Bill's coffee spill, the network will detect the lack of communication and automatically switch to the secondary ring. (This is done via protocol or hardware, depending on the infrastructure.) Now, things run normally until Bill’s computer is replaced. Once it is up and running, the network will switch to the primary ring.
High Availability, Thanks to Dual Ring Topology
Dual ring topology provides the benefit of redundancy to your network. However, there are additional benefits, such as high availability (HA).
HA is a term to describe a network’s resiliency. Dual ring topology ensures a network is up almost all of the time. This is because data always has at least one way to flow.
Dual Ring Topology Makes Load Balancing Easier
Dual ring topology does not provide load balancing in and of itself, but it can facilitate load balancing. As discussed, a DRT only has one active ring.
However, if desired, a network engineer can put the dual ring in an active-active state. This will help effectively split the load by sending packets to the closest devices instead of always circumnavigating the network.
Potential Drawbacks of Using a Dual Ring Topology
While dual ring topology has quite a few benefits, there are some potential disadvantages to using it. Let's discuss how these drawbacks may influence your decision when implementing this topology.
Dual Rings Can Be Complex and Costly
As imagined, the cost of ring topology increases significantly as more nodes are put on the network. Ring topology requires a LOT of cables and additional network devices to run efficiently. This initial capital investment may be over the line for some.
Limited Scalability with Dual Ring Topologies
Dual ring topology is challenging to scale. The more devices that are added, the more network latency is introduced. After all, if the ring is now three miles long instead of half a mile long, it will take a long time to send data from node A to node Z. Also, additional complexity is added to its overall maintenance as more nodes are added.
Can Dual Ring Topologies Have Catastrophic Failures?
Technically, yes. If both rings go down, then your network will be in serious trouble. The more nodes added, the higher the likelihood this can happen. However, it is fairly rare for both rings to go down.
What are the Alternatives to Dual Ring Topology?
While dual ring topology is great, there are alternatives worth considering. There are numerous topologies available aside from dual ring. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages compared to dual ring topology.
Star Topology vs. Dual Ring Topology
Star topology has a single node that all clients communicate with. So if one computer needs to communicate with another, the central node serves as an intermediary before the recipient node receives the data. For this to work, the central server will hopefully never go down.
Bus Topology vs. Dual Ring Topology
Bus topology is an antiquated topology that relies on a bus to send data to and from one node to the next. As an analogy, think of a pipeline connecting different floors of a skyscraper. A person will put a message into the tube, and it will stop at the intended floor.
Dual Ring Topology vs. Mesh Topology
Mesh topology is a networking strategy where every node is connected to every other node. This significantly differs from ring topology, where each node is only connected to the nearest neighbor.
Vendors of Dual Ring Topology and Alternatives
Luckily, there are plenty of vendors of dual ring topology and its alternatives.
Cisco and Dual Rings
Cisco has plenty of hardware to assist in a dual ring topology setup. For example, these switches are often used to set up a ring topology. However, Cisco also provides plenty of UCS hardware to facilitate a star topology, mesh topology, and more.
Dual Rings from Juniper
Like Cisco, Juniper offers switches specifically for ring topologies. Juniper also has a multitude of different switches, firewalls, and other hardware to meet whatever topology specification is required.
Hewlett Packard Network Solutions
Lastly, Hewlett-Packard offers some great solutions. For instance, the HPE FlexNetwork MSR series is perfect for creating ring topology networks.
The Importance of Network Topology Types
Understanding the difference between types of network topologies is one of the core tasks associated with becoming a network engineer. Now that you know more about dual ring topology, you're better prepared for on-the-job decisions about when to use dual ring versus another topology type for your network.
Ultimately, dual ring topology is great for smaller-sized networks that need redundancy and simple failover. But as the network becomes larger, dual ring topology loses its advantages.
With all that in mind, there are still plenty of topologies to learn about that we only briefly discussed here. As you study for your Network+ certification exam, you'll also run across other fundamental networking topics to know in addition to topology types. Make sure to study these, too:
Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model layers
Types of cables and connectors
Common ports and protocols
Cloud concepts and connectivity
Subnet configuration and IP addressing schemes
CBT Nuggets subscribers have access to Network+ training and resources that will help you learn these concepts and more. Create an account now — your first 7 days are free.
delivered to your inbox.
By submitting this form you agree to receive marketing emails from CBT Nuggets and that you have read, understood and are able to consent to our privacy policy.