Why Every AWS Admin Should Know Security

One of the most crucial concerns for any administrator is security. When on-prem data centers were the centerpiece of IT, sysadmins knew that it was their responsibility to protect everything from physical security (e.g., access control, fire prevention, power stability, and climate control) to maintaining antivirus software and firewalls. With the introduction of the cloud into mainstream business computing, the division of responsibilities between what sysadmins should do and what belongs to cloud infrastructure owners like Amazon and Microsoft can be a bit more muddled.
In this blog post, we'll take a look at why security is vital within Amazon Web Services (AWS) and what every AWS administrator should know about cloud security. Keep in mind that your area of responsibility for security controls varies to some degree based on whether you're using AWS Platform as a Service (PaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), or Software as a Service (SaaS) offerings.
Why is Security Important in the Cloud?
Security in the cloud is critical because of the information that's housed there. Customer databases host a plethora of personally identifiable information, company intellectual property, and other proprietary data that belongs to customers or clients. If access to any of this is compromised, the resulting data breach could cost your company hundreds of thousands or even millions of dollars. According to IBM, the average financial loss of a data breach reaches $3.86 million, clearly illustrating why security is a top priority.
In addition to general security procedures and best practices, you might need to abide by geographic- or industry-specific regulations. In the European Union, the GDPR lists detailed requirements governing personal data collection, storage, and transfer, with specific provisions for various aspects of the cloud. Businesses that work in healthcare in the United States are subject to HIPAA requirements governing how patient medical data is stored and accessed. Implementing and maintaining the proper security protocols is a crucial core responsibility for AWS admins.
However, on the other side of the equation is the need to access this information quickly and efficiently. If security were the only concern, everything would be locked down so tightly that no one could use it. Because data in the cloud must be accessed, employing security best practices while permitting maximum availability to qualified employees is still an important priority.
What Security Does AWS Provide?
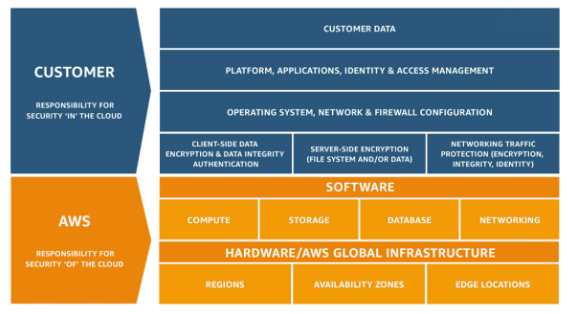
AWS operates off of a shared responsibility model, taking some responsibilities on themselves and delegating others to cloud users/customers. At a high level, Amazon provides security for protecting the infrastructure that powers the cloud. This includes hardware, software, networking, and AWS facilities where those assets are hosted. Specifically, AWS "operates, manages, and controls the components from the host operating system and virtualization layer down to the physical security of the facilities" housing the components. AWS also provides a security group firewall, although configuring and maintaining it is your responsibility as an AWS admin.
Amazon doesn’t allow cloud subscribers to visit their data centers and physically validate that appropriate security controls are in place. Still, the company does routinely hire third-party auditors to evaluate and verify compliance with industry requirements and best practices. Details can be found by visiting the Amazon site on compliance.
If you're using managed services, AWS takes on additional responsibilities for security configurations. Some of these services include Amazon DynamoDB, Amazon RDS, Amazon Redshift, Amazon EMR, and Amazon WorkSpaces. You don't have to worry about guest operating-system and database patching, firewall configuration, or disaster recovery. Depending on the service, admins may have to set up database user accounts. Beyond that, configuring access controls and safeguarding account credentials, AWS admins for these services don't have to do much.
One impressive addition to AWS-provided security is the Security Hub. This suite of detection and diagnostic tools permits you to review all high-priority security alerts, as well as compliance status across all of the AWS accounts you or your company are using. A few of these instruments include traditional offerings like Amazon GuardDuty, Amazon Inspector, and Amazon Macie, as well as more recent additions, such as Amazon Detective, AWS IAM Access Analyzer, and AWS Nitro Enclaves. AWS admins should familiarize themselves with all of these tools at a high level if only to know what Amazon provides with cloud services.
What Security Does an AWS Admin Provide?
AWS admins have varying responsibilities depending on what services they use. For AWS managed services, admins are required to do very little. However, if you're deploying Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2, which is IaaS), the responsibility swings the other way, and an admin's requirements substantially increase. With IaaS, customers are "responsible for management of the guest operating system (including updates and security patches), any application software or utilities installed by the customer on the instances, and the configuration of the AWS-provided firewall (called a security group) on each instance."
Numerous tasks fall into the realm of "shared controls." For example, when it comes to patch management, Amazon will patch and address any flaws within the infrastructure, but customers must repair their guest operating systems and applications. Configuration management is also divided: while Amazon handles all configuration for the AWS infrastructure, areas such as guest OS, databases, and applications fall on the customer sysadmins.
Security zones and any other company-specific requirements or protocols always fall to the AWS admin. Industry requirements (e.g., HIPAA, GDPR) are not Amazon's concern, nor is AWS training for your company's employees. Although Amazon provides a robust suite of detection tools, monitoring and responding to them is the customer's responsibility.
As an AWS admin, it's your obligation to implement your company's security structure — whether you're a security newbie or a seasoned pro. This includes configuring access policies and ensuring that your users abide by company and industry requirements. Activity log review, intrusion detection, and evaluating unusual activity for further investigation fall under a sysadmin's purview as well. Finally, having a plan in place to respond to any incidents is also something a customer must do.
Establishing Your Role as an AWS Admin Security Provider
The basic philosophy behind the shared responsibility model is security "of" the cloud (AWS) versus security "in" the cloud (the customer). Generally speaking, anything you're unable to access or control falls under Amazon's purview (such as physically configuring hardware). At the same time, any unique configurations to your company or industry will be your responsibility.
Final Thoughts
We often hear the question, "As an AWS administrator, why should I know about security?" Amazon has done an excellent job of dividing security roles appropriately between itself and AWS administrators. The tools in the AWS Security Hub provide everything you need to maintain a safe and secure environment as long as you use them appropriately. The best thing you can do as an AWS admin is to acquaint yourself thoroughly with the provider's security processes for the specific services your company is using.
You should adopt a "trust but verify mindset," where you fully believe that AWS will do its due diligence. Still, you also review each aspect of your company’s cloud security to ensure that everything operates effectively. The tools in AWS’s Security Hub are ones with which you should be intimately familiar: review them all, configure the ones most appropriate to your use, and keep the others referenced in the back of your mind. You want your system to be as fault-tolerant as possible. As your company's cloud presence grows, so will your need to oversee more security protocols.
delivered to your inbox.
By submitting this form you agree to receive marketing emails from CBT Nuggets and that you have read, understood and are able to consent to our privacy policy.